World Electric Vehicle Journal : Thermal Analysis of Coupled Resonant Coils for an Electric Vehicle Wireless Charging System
Authors: Chunming Wen, Qing Xu, Minbo Chen, Zhanpeng Xiao, Jie Wen, Yunyun Luo, Xiaohui Zhao, Yuanxiong Liang, and Kairong Liang
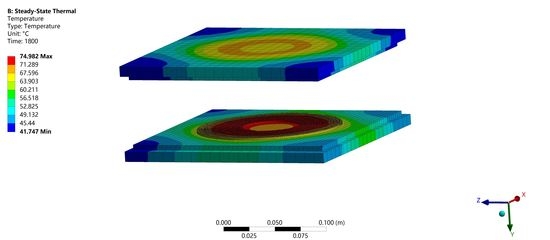
Electric vehicles use wireless energy transmission to obtain energy, which can effectively avoid the shortcomings of traditional methods. As the carrier of radio energy transmission and reception, the high temperature of the coil triggers the degradation of wireless transmission performance and the aging of the coil, which may cause fire and other safety problems in serious cases. This paper studied the temperature distribution of the magnetically coupled coil model for electric vehicles. Based on the study of the basic law of heat transfer, the coil model was established using ANSYS software, and the boundary conditions and relevant parameters were set. After many simulation experiments and comparisons, it was finally determined that the transmitting coil and the receiving coil were the same sizes, the inner diameter of the coil was 100 mm, the outer diameter of the coil was 181 mm, and the coupling distance between the transmitting coil and the receiving coil was set to 60 mm. Coil models were simulated and analyzed using different materials. The simulation results show that after 30 min of system operation, the material chosen from the temperature range may have been gold, silver, copper, or aluminum, but from the comprehensive consideration of cost and performance, the material of the coil in the model was finally set to copper. Copper was the best material; its temperature maximum was 74.952 °C and lower than the safety value of 80 °C. It is hoped that this study will provide a reference for wireless charging coil design.
In the same category
- “Driving Collaboration in Europe's Thriving EV Sector: opportunities for emissions reductions”
- Autel Energy bringing innovative new EV chargers across Europe
- Baden-Württemberg on its way to becoming the top location for e-mobility
- ECO/G
- Empowering the Transition to Electric Mobility: Equans' Smart Charging Solutions
- Hyundai
- Leapmotor
- Sungrow EV Charging Introduced Low and Fast EV Charging solutions
- Total Energies
- Why Submit to World Electric Vehicle Journal?
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Analysis of Energy Flow in a Mid-Sized Electric Passenger Vehicle in Urban Driving Conditions
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Battery Health Monitoring and Degradation Prognosis in Fleet Management Systems
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Evaluation of a Back-up Range Extender and Other Heavy-Duty BEV-Supporting Systems
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Implementation Schemes for Electric Bus Fleets at Depots with Optimized Energy Procurements in Virtual Power Plant Operations
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Investigation and Development of Textile Lightweight Bodies for Urban Logistic Vehicles
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Leveraging Connected Vehicle Data to Assess Interstate Exit Utilization and Identify Charging Infrastructure Investment Allocation Opportunities
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Performance Comparison of Si IGBT and SiC MOSFET Power Module Driving IPMSM or IM under WLTC
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Perspectives on Modeling Energy and Mobility Transitions for Stakeholders: A Dutch Case
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Proposing a Hybrid Thermal Management System Based on Phase Change Material/Metal Foam for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Second-Life Batteries Modeling for Performance Tracking in a Mobile Charging Station
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : The “Semiconductor Crisis” as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Impacts on the Automotive Industry and Its Supply Chains
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Thermal Analysis of Coupled Resonant Coils for an Electric Vehicle Wireless Charging System