Hyundai
Hyundai is one of Europe’s leading EV manufacturers, as it transitions to becoming a Smart Mobility Solutions Provider. The company is demonstrating its leadership in e-mobility and the creation of sustainable societies by pioneering innovative technologies like Vehicle-to-Load and Vehicle-to-Grid.
The strong commitment to innovation, progress, and sustainability has driven Hyundai Motor Europe’s success as a leader in electrification. Having laid down a marker with the 2016 launch of the original IONIQ model, the electrified products and concepts that have followed since align with the company’s vision of “Progress for Humanity” and its ambition to improve the communities in which it operates – for people today and for generations to come.
Hyundai is driving innovation in the field of electrified mobility with the development of its pioneering technologies. The entire IONIQ line-up brand is built on Hyundai Motor Group’s state-of-the-art Electric-Global Modular Platform (E-GMP), including respective World Car of the Year 2022 and 2023 winners, IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 6, as well as IONIQ 5 N, Hyundai’s first high-performance, mass-production model.
E-GMP, designed exclusively for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs), offers an array of lifestyle benefits for customers. The platform’s electrified advantages include a competitive all-electric range, 800V high-speed charging capabilities, a multi-charging system, and two ports for the Vehicle-to-Load (V2L) function. E-GMP’s structure allows for human-centric interior design, modularised parts, maximised space, and a strengthened steel frame.
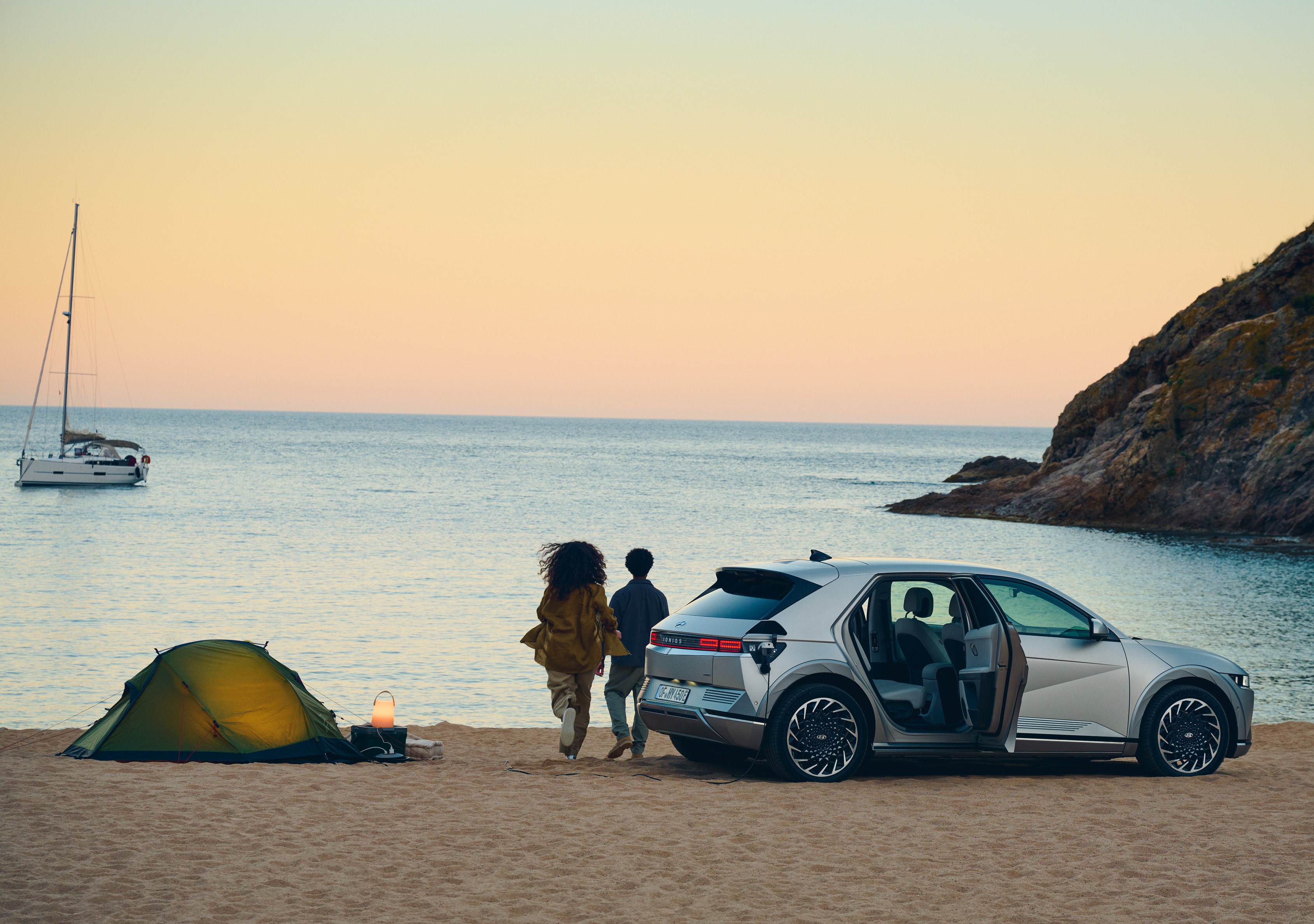
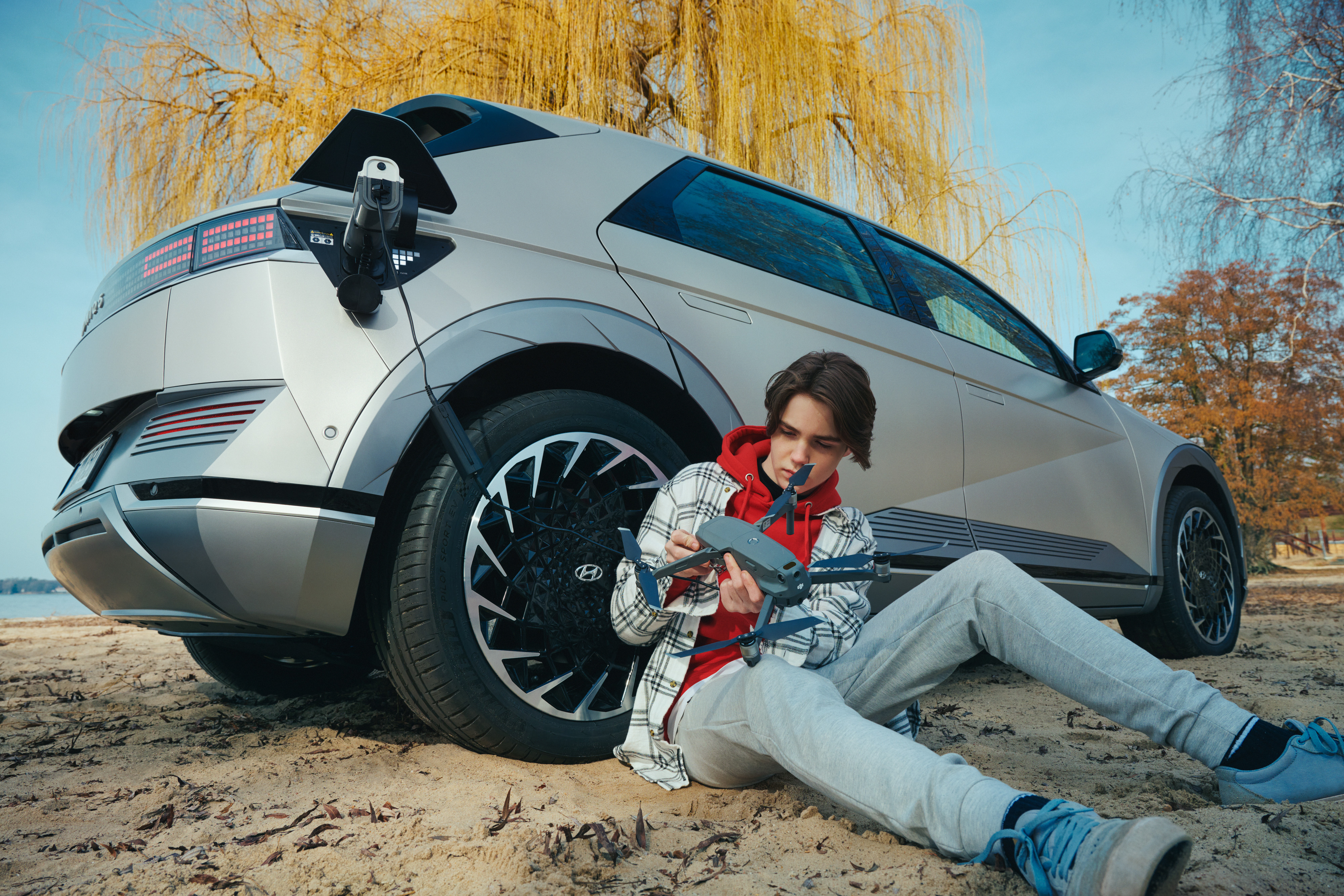
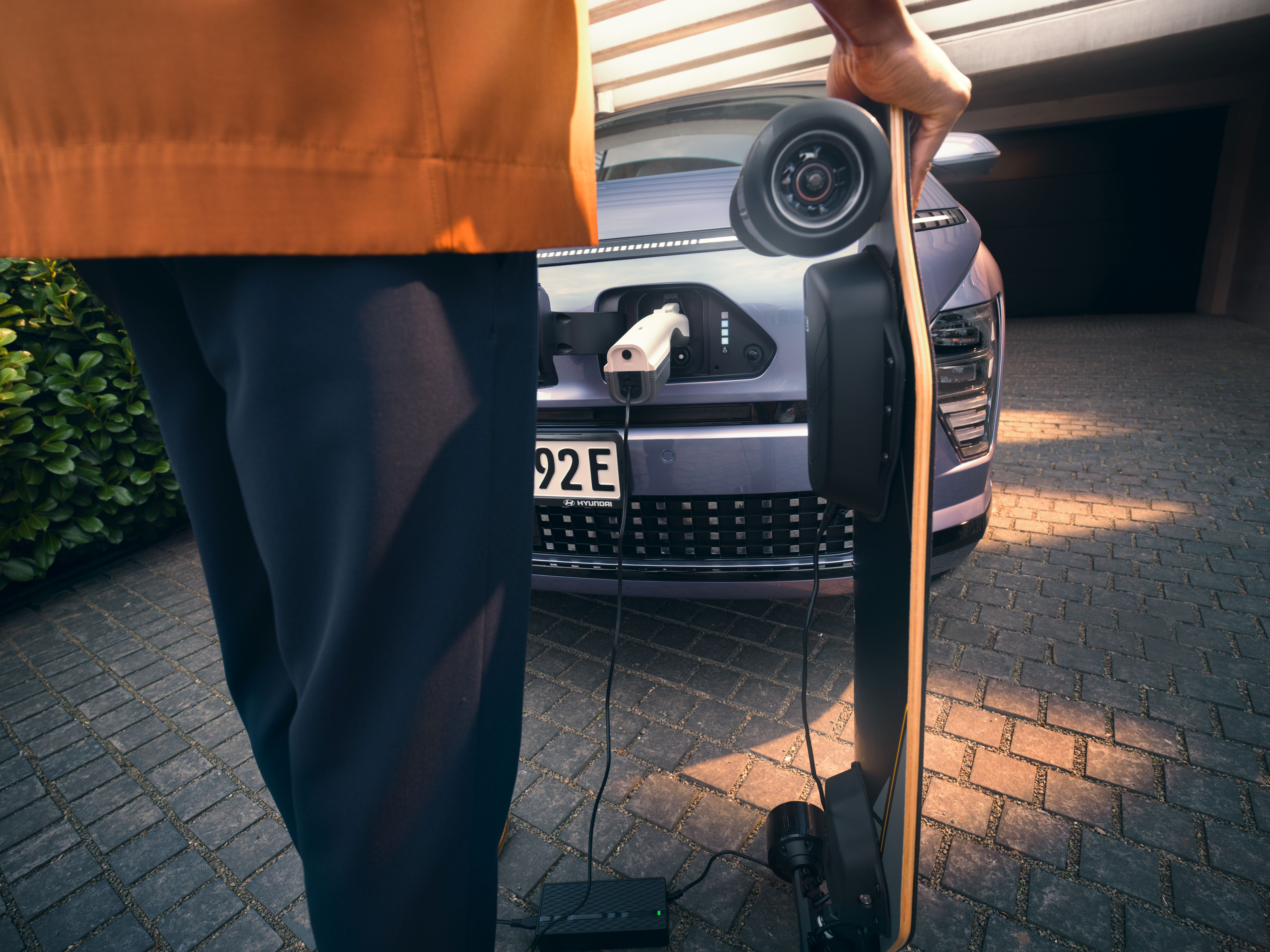
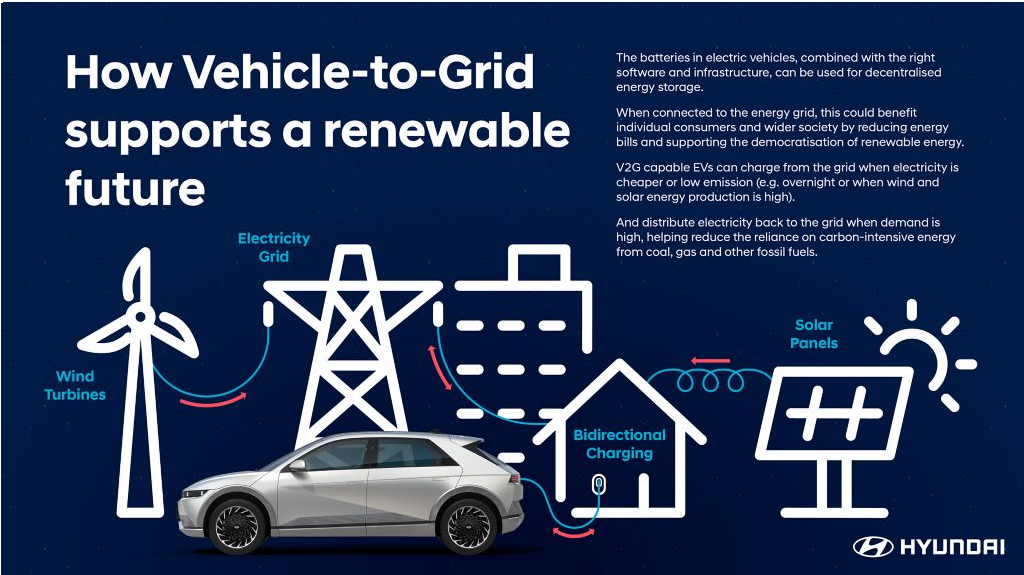
The company brought bidirectional charging to the market through its next-generation BEVs. Bidirectional charging refers to energy transfer, in which the energy stored in the battery pack of an EV can be transferred to an electronic device. For the first time in a commercially available electric car, Hyundai pioneered the innovative V2L function – revealed in the 2021 launch of IONIQ 5. Since then, the V2L function is also available in IONIQ 6 and the second-generation Kona Electric, which celebrated its premiere earlier this year.
V2L technology redefined electric mobility lifestyles in more ways than one, allowing customers to freely power or charge any electronic device and effectively use the vehicle as a power bank on wheels. However, the possibilities can go even further: V2L has the potential to replace generators powered by petrol, diesel, oil, or any other unsustainable source. The technology can reduce range anxiety in an area with fewer charging or power opportunities because it can be used between two BEVs. V2L can offer BEV customers more freedom than ever before.
Over the past two years, Hyundai has further developed Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology – another innovation based on bidirectional charging. This technology enables the energy that is already stored in the battery packs of BEVs to be provided to an electricity network and can help countries diversify their energy mix to include more renewable energy sources.
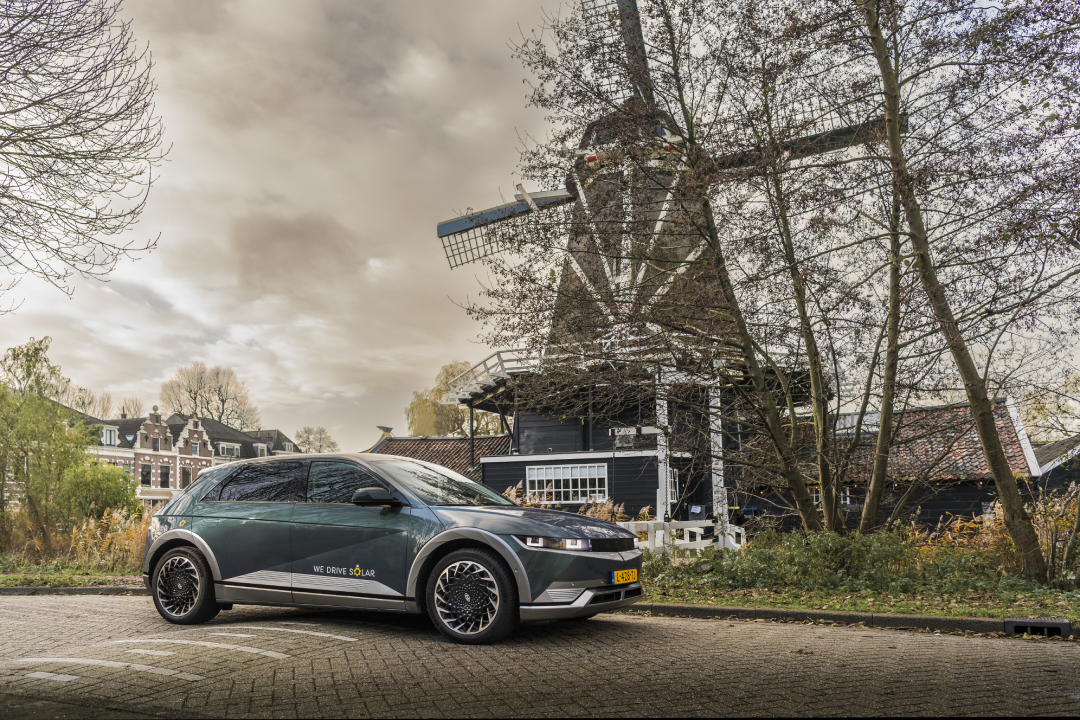
To demonstrate the potential of V2G technology, in early 2022, Hyundai launched an innovative mobility pilot project in Utrecht, together with the local mobility provider We Drive Solar. To support Utrecht’s ambition to become the world’s first bidirectional region, Hyundai is deploying a fleet of IONIQ 5 units equipped with V2G technology for a car-sharing scheme serving residents in the city’s new Cartesius development district.
Hyundai also launched a V2G proof of concept project in Germany, coordinated by CRADLE Berlin, Hyundai Motor Company’s corporate venturing and open innovation business. The project tested the ability of the IONIQ 5 to share energy with the grid within a closed home energy system.
With innovative technologies like E-GMP, V2L, and V2G, Hyundai is speeding up its transition to becoming a Smart Mobility Solutions Provider. The company continues to demonstrate its leadership in electric mobility and sustainability, striving to secure a position as one of the leading EV manufacturers in Europe.
In the same category
- “Driving Collaboration in Europe's Thriving EV Sector: opportunities for emissions reductions”
- Autel Energy bringing innovative new EV chargers across Europe
- Baden-Württemberg on its way to becoming the top location for e-mobility
- ECO/G
- Empowering the Transition to Electric Mobility: Equans' Smart Charging Solutions
- Hyundai
- Leapmotor
- Sungrow EV Charging Introduced Low and Fast EV Charging solutions
- Total Energies
- Why Submit to World Electric Vehicle Journal?
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Analysis of Energy Flow in a Mid-Sized Electric Passenger Vehicle in Urban Driving Conditions
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Battery Health Monitoring and Degradation Prognosis in Fleet Management Systems
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Evaluation of a Back-up Range Extender and Other Heavy-Duty BEV-Supporting Systems
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Implementation Schemes for Electric Bus Fleets at Depots with Optimized Energy Procurements in Virtual Power Plant Operations
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Investigation and Development of Textile Lightweight Bodies for Urban Logistic Vehicles
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Leveraging Connected Vehicle Data to Assess Interstate Exit Utilization and Identify Charging Infrastructure Investment Allocation Opportunities
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Performance Comparison of Si IGBT and SiC MOSFET Power Module Driving IPMSM or IM under WLTC
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Perspectives on Modeling Energy and Mobility Transitions for Stakeholders: A Dutch Case
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Proposing a Hybrid Thermal Management System Based on Phase Change Material/Metal Foam for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Second-Life Batteries Modeling for Performance Tracking in a Mobile Charging Station
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : The “Semiconductor Crisis” as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Impacts on the Automotive Industry and Its Supply Chains
- World Electric Vehicle Journal : Thermal Analysis of Coupled Resonant Coils for an Electric Vehicle Wireless Charging System



