Comparative Study of Permanent Magnet, Conventional, and Advanced Induction Machines for Traction Applications
This paper investigates and compares the torque-generating capabilities and electromagnetic performance of advanced non-overlapping winding induction machines (AIM), conventional induction machines (CIM), and interior-permanent magnet (IPM) machines for electric vehicle (EV) applications.
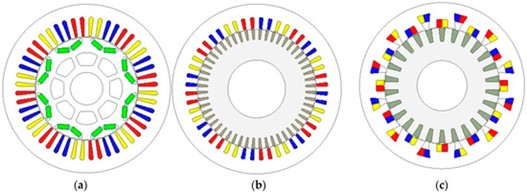
Figure 1. Two-dimensional views of the compared machines: (a) IPM (48S/16M/8P). (b) CIM (48S/52R/8P). (c) AIM (24S/26R/8P).
All investigated machines are designed based on the specifications of the Toyota Prius 2010 IPM machine. The steady-state and flux-weakening performance characteristics are calculated by employing the 2D finite element method and MatLab, and the obtained results are quantitatively compared. Furthermore, the torque-generating capabilities of three machines are investigated for different electric loadings, and the machine having the highest torque-generating capability is determined as AIM. Moreover, the major parameters affecting the torque-generating capability, such as magnetic saturation and magnet demagnetization, are examined in depth.
Authors: Tayfun Gundogdu,Zi-Qiang Zhu, and Ching Chuen Chan
In the same category
- A Smart Battery Management System for Electric Vehicles Using Deep Learning-Based Sensor Fault Detection
- Autel Energy Europe at AEC 2024: Pioneering the Future of Ultra-Fast EV Charging
- Baden-Württemberg International: Your partner for a successful expansion
- Business Region Goteborg : Gothenburg - Pioneering tomorrow's mobility
- Charging Electric Vehicles Today and in the Future
- Comparative Study of Permanent Magnet, Conventional, and Advanced Induction Machines for Traction Applications
- Design Methodology and Circuit Analysis of Wireless Power Transfer Systems Applied to Electric Vehicles Wireless Chargers
- Designing High-Power-Density Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles with Advanced Magnetic Materials
- Energy and Environmental National Assessment of Alternative Fuel Buses in Morocco
- Energy Management and Optimization of Large-Scale Electric Vehicle Charging on the Grid
- Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Review of Topologies and Energy Management Strategies
- Numerical Simulation of Cooling Plate Using K-Epsilon Turbulence Model to Cool Down Large-Sized Graphite/LiFePO4 Battery at High C-Rates
- Using an Intelligent Control Method for Electric Vehicle Charging in Microgrids
- Will Utrecht become the world's first bidirectional city?